녕의 학습 기록
백준_17472_다리 만들기 2 (mst&bfs) 본문
자력으로 풀어내서 매우 뿌듯ㅋ
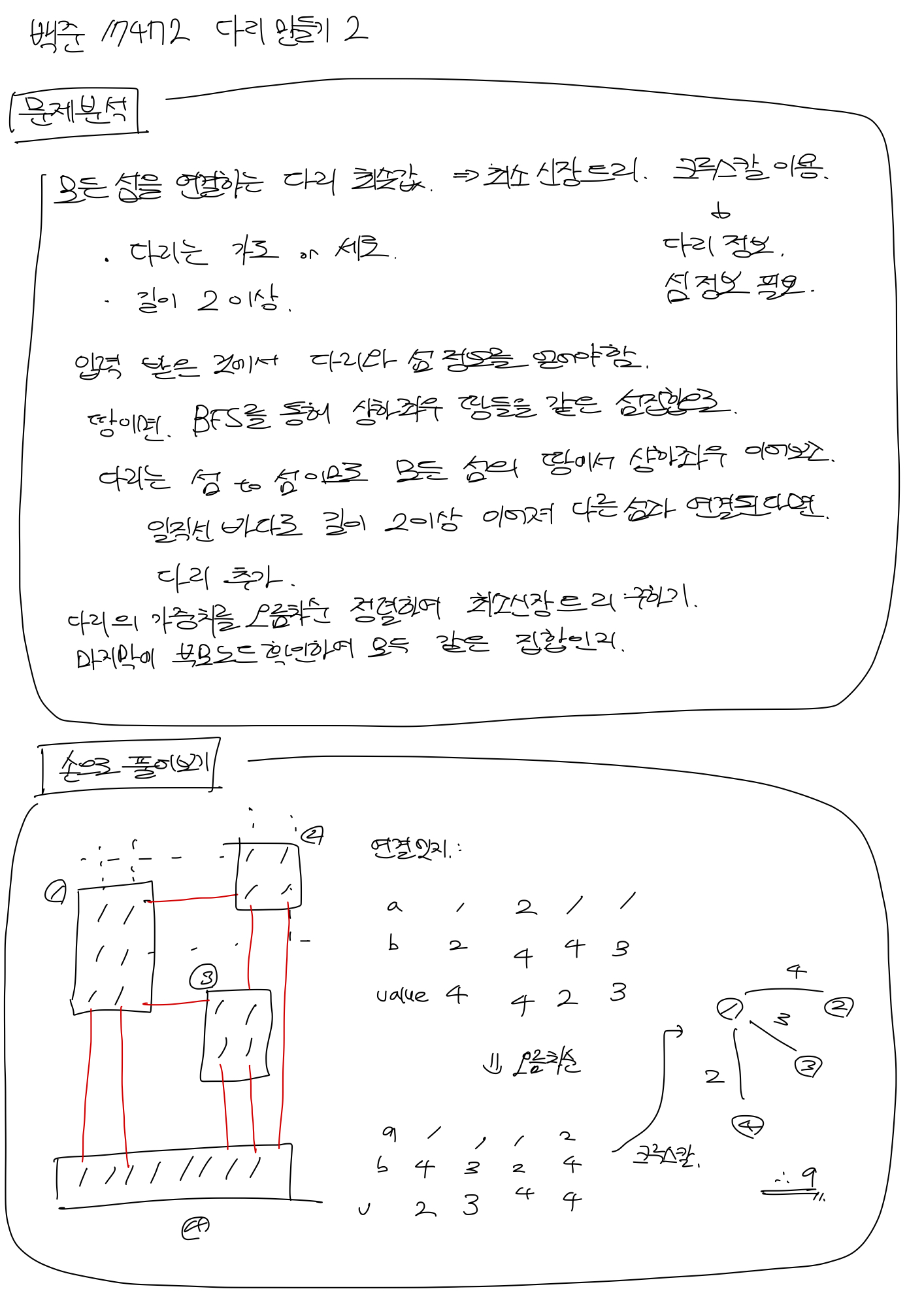

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BJ_17472_다리만들기2 {
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1}; //상하좌우
static int[] dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] parent;
static int[][] map;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> edges;
static boolean[][] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[n][m];
visited = new boolean[n][m];
int i, j;
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
for (j=0; j<m; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int d, nextGndM, nextGndN;
int island = 0;
Queue<int[]> queue;
//섬 구분
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
//방문 안한 땅이면 새로운 섬으로 간주하고 bfs
if (visited[i][j] == false && map[i][j] == 1) {
island++; //섬 개수 겸 번호 증가
queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
visited[i][j] = true;
map[i][j] = island; //섬번호 입력
int[] nowGnd;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
nowGnd = queue.poll();
for (d = 0; d < 4; d++) { //상하좌우
nextGndN = nowGnd[0] + dy[d];
nextGndM = nowGnd[1] + dx[d];
if (nextGndM >= 0 && nextGndM < m &&
nextGndN >= 0 && nextGndN < n) { //좌표 유효성 체큰
//방문하지 않은 땅이면 같은 섬의 땅이므로 큐에 추가
if (visited[nextGndN][nextGndM] == false
&& map[nextGndN][nextGndM] != 0) {
visited[nextGndN][nextGndM] = true;
map[nextGndN][nextGndM] = island;
queue.add(new int[]{nextGndN, nextGndM});
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//island는 앞에서 bfs 진행한 횟수이자 섬 개수
parent = new int[island+1];
for (i=1; i<island+1; i++) { //섬의 부모 노드 초기화
parent[i] = i;
}
edges = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Edge>() {
@Override
public int compare(Edge o1, Edge o2) {
return o1.value - o2.value;
}
});
//섬으로부터 다른 섬으로 이루어지는 다리 구하기
int nowGndN, nowGndM, nowIsland, nextIsland;
int value; //다리의 가중치
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (j=0; j<m; j++) {
if (map[i][j] != 0) { //땅에서
nowGndN = i;
nowGndM = j;
for (d=0; d<4; d++) { //상하좌우로 이동
nextGndN = nowGndN + dy[d];
nextGndM = nowGndM + dx[d];
value = 0;
nowIsland = find(map[nowGndN][nowGndM]);
//좌표가 유효한 동안 한 방향으로 이동
while(nextGndM >= 0 && nextGndM < m && nextGndN >=0 && nextGndN < n){
//땅이 나오면(섬이 나오면)
if (map[nextGndN][nextGndM] != 0) {
nextIsland = find(map[nextGndN][nextGndM]);
//다른 섬이고, 거리가 2 이상이면 다리 추가
if (nowIsland != nextIsland) {
if (value > 1) {
edges.add(new Edge(nowIsland, nextIsland, value));
}
}
break;
} else { //바다인경우 계속 한방향으로 진행
nextGndN += dy[d];
nextGndM += dx[d];
value++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
int edgeCnt = 0;
int result = 0;
while (edgeCnt < island-1 && !edges.isEmpty()) {
Edge nowEdge = edges.poll();
//사이클 x이면 연결
if (find(nowEdge.a) != find(nowEdge.b)) {
union(find(nowEdge.a), find(nowEdge.b));
result += nowEdge.value;
edgeCnt++;
}
}
//모든 섬이 연결되어있는지 체크
int temp = find(1);
for (i=2; i<island+1; i++) {
if (find(i) != temp) { //연결되어있지 않음
System.out.println(new StringBuilder().append(-1));
return;
}
}
System.out.println(new StringBuilder().append(result));
}
static int find(int a) {
if (parent[a] == a) {
return a;
} else {
int temp = find(parent[a]);
parent[a] = temp;
return temp;
}
}
static void union(int a, int b) {
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if (a!=b) {
parent[b] = a;
}
}
static class Edge {
int a;
int b;
int value;
public Edge(int a, int b, int value) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.value = value;
}
}
}17472번: 다리 만들기 2
첫째 줄에 지도의 세로 크기 N과 가로 크기 M이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 지도의 정보가 주어진다. 각 줄은 M개의 수로 이루어져 있으며, 수는 0 또는 1이다. 0은 바다, 1은 땅을 의미한다.
www.acmicpc.net
'Algorithm > Algorithm 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준_11725 트리의 부모 찾기 (트리, dfs) (0) | 2024.03.05 |
|---|---|
| 백준_1414 불우이웃돕기 (mst) (0) | 2024.03.04 |
| 백준_1197_최소스패닝트리 (mst) (1) | 2024.03.02 |
| 백준_1389 케빈 베이컨의 6단계 법칙 (플로이드-워셜) (1) | 2024.02.29 |
| 백준_11403 경로 찾기 (플로이드-워셜) (1) | 2024.02.28 |




